Material Process of SMT Nozzles
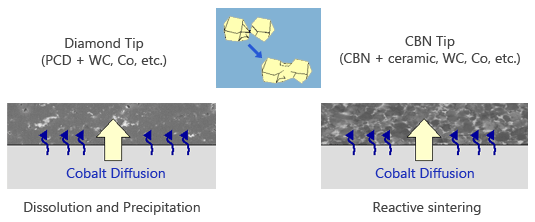
Since the melting points of the nozzle components such as tungsten carbide (WC), zirconia (ZrO2) are too high and the reaction occurs when melting such as dissolution and precipitation between diamond (carbon) and cobalt (Co), PM is a feasible process to use.
Nozzle Tip – Powder Metallurgy (PM)
Nozzle Body – PM or use general steel alloys such as stainless steel.
1. Introduction of Powder Metallurgy (PM)
PM Process
Pressing - Powders are compressed into the desired shape in a press-type machine using punch-and-die tooling designed specifically for the part.
Sintering - Heating at a temperature well below melting.
Advantage
Near-net shape, No waste, Controlled porosity, Dimension control better than casting
Disadvantage
High cost of tooling and powder, Powder Harder to handle Geometric & Size limitation, Density variation
Particle Shapes and Sizes
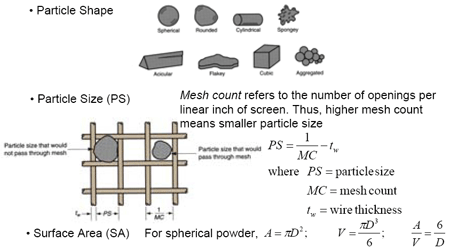
Morphology (Particle Shapes)
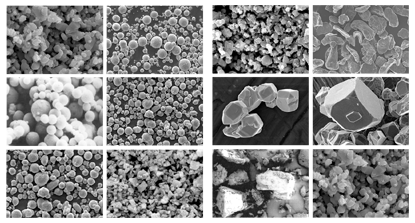
2. PM materials for SMT nozzles
Various materials can be adopted for forming a nozzle tip or a nozzle body:
Principal component: polycrystalline diamond (PCD), monocrystal diamond, diamond created by physical vapor deposition (PVD), diamond created by chemical vapor deposition (CVD), diamond like carbon (DLC), carbonado, cubic boron nitride (CBN), hexagonal boron nitride, zirconia, or a combination of these
Refractory component: tungsten carbide, titanium carbide, tantalum carbide, zirconium carbide, hafnium carbide, chromium, titanium, vanadium, niobium, aluminum, nickel, hafnium, silicon, tungsten, molybdenum, or alloys including one or more of these
Solvent-Catalyst Metal (binder): cobalt
Considered material properties: Modulus, Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), Dilatoric and Deviatoric Stresses, Free Voulume Reduction of each powder, etc.
| Material | Specific Gravity | Hardness (Knoop) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m K) | CTE (x10-6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) | 3.5 - 4.0 | 7000 | 900 | 1.5 - 4.8 |
| Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) | 3.48 | 4500 | 800 | 1.0 - 4.0 |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | 3.5 | 3000 | 7.8 - 8.8 | |
| Tungsten Carbide (WC) (10% Co) | 14.6 | 2200 | 112 | 4 - 6 |
Requested purposes for SMT nozzle tips
Abrasive resistance and Hardness, Impact strength and Toughness, Whitening event (to reduce)
* Whitening event: As being used, a nozzle tip turns from black to white due to wearing, contaminating by solder paste.
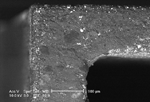
Abrasion

Fracture
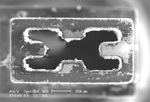
Whitening event
3. CROSTU's SMT Nozzle Materials & PM Process

| Type | Components | Production Process | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nozzle Tip | Diamond Tip | PCD + Carbide, Cobalt, etc. | PM |
| CBN Tip | CBN + Ceramic, Carbide, Cobalt, etc. | PM | |
| Ceramic Tip | Zirconia + Carbide, Cobalt, etc. | PM | |
| Nozzle Body | Superhard material | Tunsten carbide + Cobalt | PM |
| Steel Alloys | Stainless steel or others | Ingot material |
SMT nozzle PM Process
Raw materials (PCD, WC, Co) → Milling → Drying → CIP (Shrinkage rate, Dimension) → Sintering (Hot Isostatic Pressing, HIP) → Machining → Nozzle tip disc / Nozzle body rod
Sintering mechanism
PM products
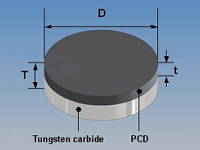
Nozzle tip disc
Nozzle tip after machining tip disc

Nozzle body rods